One of the most common childhood fears is going to the dentist. Who would not relate? Sitting in a huge chair illuminated by blinding light, enduring lengthy seated sessions with someone looking and poking inside your mouth using edgy and frightening devices, producing sounds like the screams of tortured souls from hell. And finally, when the misery is over, that same someone tells you not to eat your favourite sweets and instructs you to brush your teeth regularly.
We’ve all been through this as a kid and childhood memories stick with us, just recalling this might send a shiver down your spine. No one likes to go to the dentist in spite of the fact that everyone knows how crucial oral health is and how strongly it is connected to our overall health. But an armada of new technologies from virtual reality through artificial intelligence (A.I.) to CRISPR will revolutionise dentistry and our whole attitude towards oral health in the future.
Just like in the case of other medical specialties, disruptive innovations will have a huge impact on how dentistry will be practised and how patients will take care of themselves in the future. Can you imagine that you might get your 3D-printed prosthesis in an hour instead of 4-5 sessions at the dentist? How about having a teledentist consultation? Or being able to grow new teeth at the age of 80?
Let’s see how these can be the case in the future thanks to the following 9 technologies.
1. Artificial intelligence
Already, dentists employ software to get insights into clinical decision-making. These will develop further to integrate A.I. algorithms to enable clinicians to find the best modalities for their patients.
Authors of a 2019 study write that with the exponential rise in health data and the maturing of healthcare A.I., dental medicine is entering a new stage of its digitisation. Such smart algorithms can be integrated within the healthcare system to analyse health data, research findings and treatment techniques to offer diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations for individual patients.
This will be made further possible with the accumulation of health data; in particular, genomic data, that can offer a deeper understanding of each individual’s system for personalised care. With A.I. tools having access to such information, they can instantly offer the best treatment options and probabilities of success to the clinicians.
On top of churning health data, A.I.-based algorithms can help specialists better tend to dental conditions. Researchers in 2019 developed a machine learning method to accurately quantify immune cells in the vicinity of oral cancer cells. This gives better insights into the spread of and resistance to cancer; thereby helping in determining the chances of survival. Others are using neural networks to better detect dental decay and periodontal disease from radiographs. Such approaches can become standard practice in the near future.
However, as the field of dental medicine is exploring the potential beneficial uses of digital data both for dental practice and in research, digitalisation is raising numerous novel and unpredictable ethical challenges in the biomedical context. This 2020 study aimed to map the debate on the currently discussed ethical issues in digital dentistry through a systematic review of the literature
2. Smart toothbrush
Our home will be filled with connected, smart devices in the future, so why would our bathroom be an exception. At first, it might feel a bit strange to let a sensor into one of your most intimate activities, tooth brushing, but it makes a lot easier to maintain oral hygiene and prevent plaque or cavities.
The Kolibree smart electric toothbrush makes sure you are brushing your teeth the right way through its app and offers kids fun games to keep up the good habit of regularly cleaning their teeth. Philips’ Sonicare smart toothbrush comes packed with sensors in its handle. These provide real-time feedback via a companion app warning you if you are applying too much pressure, where you are brushing and even coach the user as to how to brush properly. And there are several such devices on the market from companies like Colgate and Oral-B.
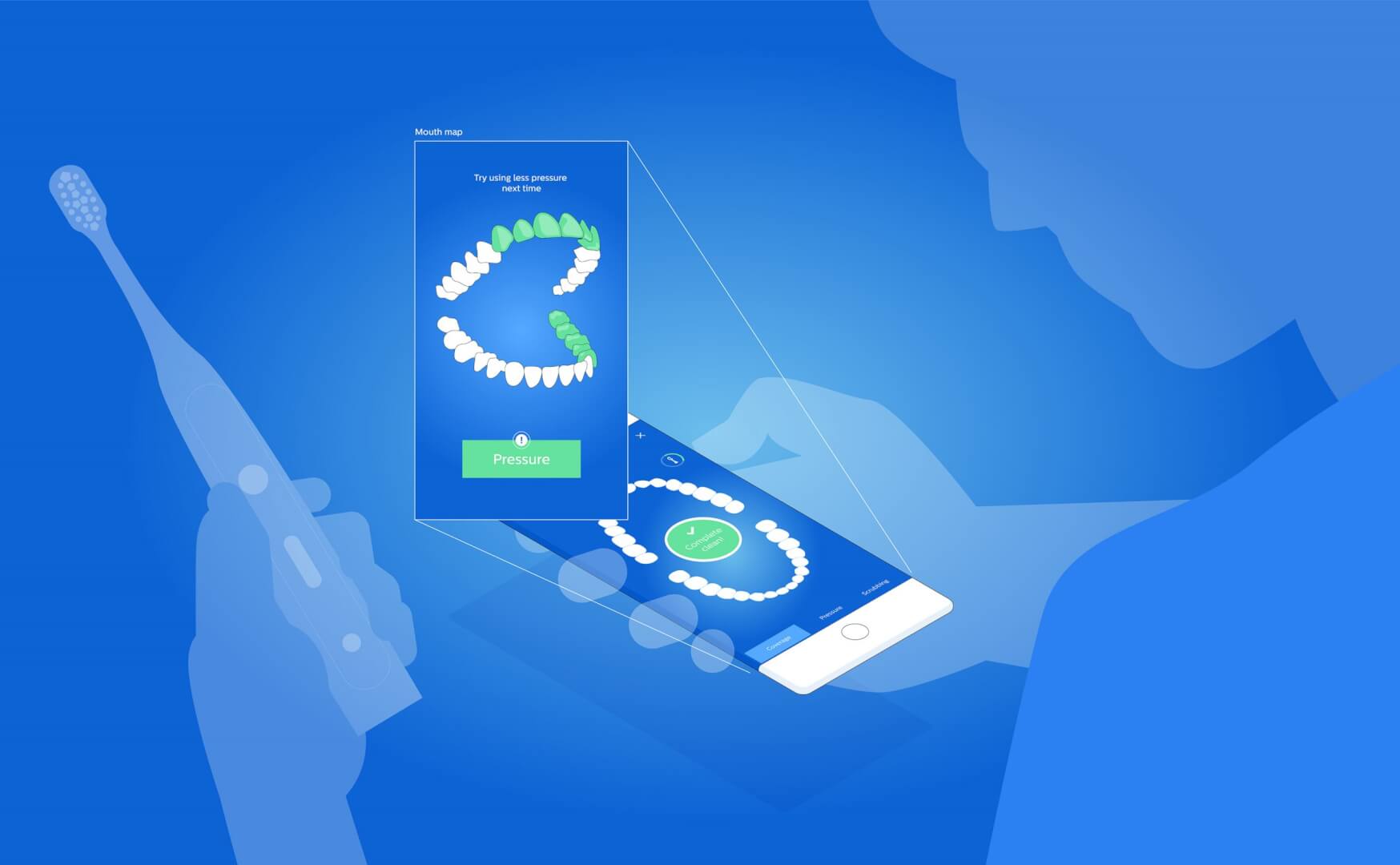

While having a personal coach to optimise your daily oral hygiene might sound enticing, not everyone is enthusiastic about the technology. Firstly, dental experts emphasise the need for proper brushing techniques which these devices won’t improve upon. Rather, it’s a dental professional who can demonstrate the proper techniques at your next appointment.
Additionally, by buying smart toothbrushes from companies like Procter & Gamble and Philips Oral Healthcare you agree to their privacy policies that enable them to share your data with third parties. Now that health data is the new oil, companies will want to profit off of these in as many ways as possible. So you might want to adopt a smart toothbrush from a company that gives you more control over your data or one that doesn’t share it with third parties at all.
3. Augmented Reality
You might be familiar with Augmented Reality (AR) through social media apps; it’s the same technology that Snapchat uses to superimpose filters on your face during your guilt trip selfie with a dog face filter. But AR also found a home in dentistry for both educational and clinical purposes.
Image Navigation’s DentSim Simulator pairs AR with a mannequin on which students can perform procedures while receiving immediate feedback as their movements are tracked. This helps them identify faster where they should improve and develop their skills in the process. It’s already in by 8 500 students in dental schools around the world.
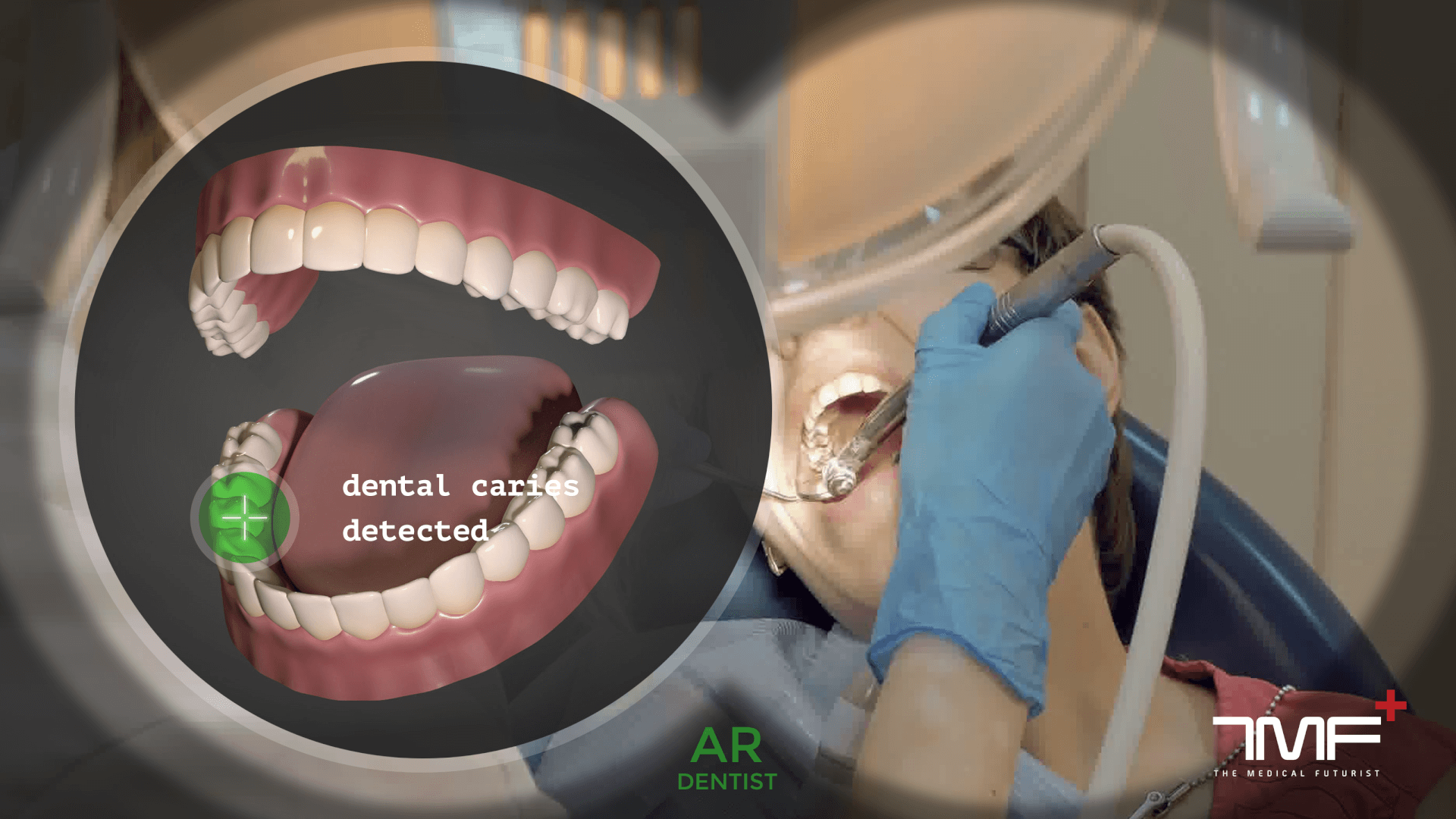
In dental practice, the technology is more prevalent in reconstructive and aesthetic procedures in order to help patients know what they will look like after the treatment. SmartTek and Kapanu have developed such AR apps that use their phone or tablet’s camera to overlay virtual depictions of the improved set of teeth prior to the procedure. This allows patients and dentists to configure features of their teeth such as height and spacing to their liking before they even enter the surgery room.
4. Virtual Reality in dentistry
Not to be confused with AR, Virtual Reality (VR) completely closes off the outside world with a dedicated headset and immerses the user in a virtual environment. By slipping such a headset on their head, students and aspiring dental surgeons can be transported to the OR from their couch; while patients can visualise a calming landscape while seated at the dreaded dentist’s chair to improve their experience.
Today, only a few students can peek over the shoulder of the surgeon during an operation and it is challenging to learn the tricks of the trade like that. With a virtual reality camera, surgeons can stream operations globally and allow medical students to actually be there in the OR using their VR goggles. Dentistry even outpaced other fields of medicine in adopting this method. Back in 2015, Nobel Biocare held the first dental surgery filmed through VR and allowed observers to virtually assist the whole procedure from the surgeon’s perspective. In comparison, the first VR-recorded surgery was performed at the Royal London hospital in 2016. The technology can further be used to help dentists build on their empathy skills through simulations putting them in the shoes of their patients or in challenging situations.
On the patient side, VR might be the solution to our dentist’s office anxiety. An experiment with 69 participants showed that VR can be used as an effective distraction tool in dentistry. Patients wore goggles which displayed calming natural scenes, and remembered the treatments more positively afterwards. OperaVR is one such VR tool for reducing dental anxiety.
5. Teledentistry
If you are reluctant to go to the dentist, imagine how hard it is for children, patients with special needs or the elderly in nursing homes. Another issue is distance: people living in rural areas rarely get access to a dentist, and almost never have the possibility of choice. This can change significantly with the spread of teledentistry.
Teledentistry services offered by companies like The Teledenists and MouthWatch provide easier access to oral and dental care; are significantly cheaper for patients; shift towards cheaper prevention practices; and allow patients to consult with otherwise unavailable medical professionals. For instance, MouthWatch’s TeleDent service offers an all-in-one teledentistry platform allowing patients to capture images, send relevant information to a dentist remotely and do a live consult. The dentist might start a video chat with the patient and the caregiver so that the medical professional can actually see and talk to the patient, build rapport, help connect them and bring them into the office (if necessary).
As remote care’s importance swelled during the pandemic, teledentistry is also picking up steam and authorities are responding accordingly. The American Dental Association issued a policy on teledentistry that offers guidance on the modalities that such services can follow. This sets the pace in making teledentistry a general practice.
6. Computer-assisted design and 3D-printing
3D-printing does not need any introduction considering the buzz it generated in healthcare a while ago with the technology’s potential to print medicines, prosthetics and even organ replicas. Its importance was further highlighted during the COVID-19 crisis to bypass supply chains to meet hospitals’ demands. As the technology is set to become an integral part of healthcare practice, it will also become incorporated in dental labs.
Computer-assisted design (CAD) and computer-assisted manufacture (CAM), including 3D-printing, are already revolutionising the sector; they are turning them into low-cost, more effective digital labs. Traditionally, when a patient needs a crown, a dentist must make a mould of the tooth and fashion a temporary crown, then wait for the dental laboratory to make a permanent one.
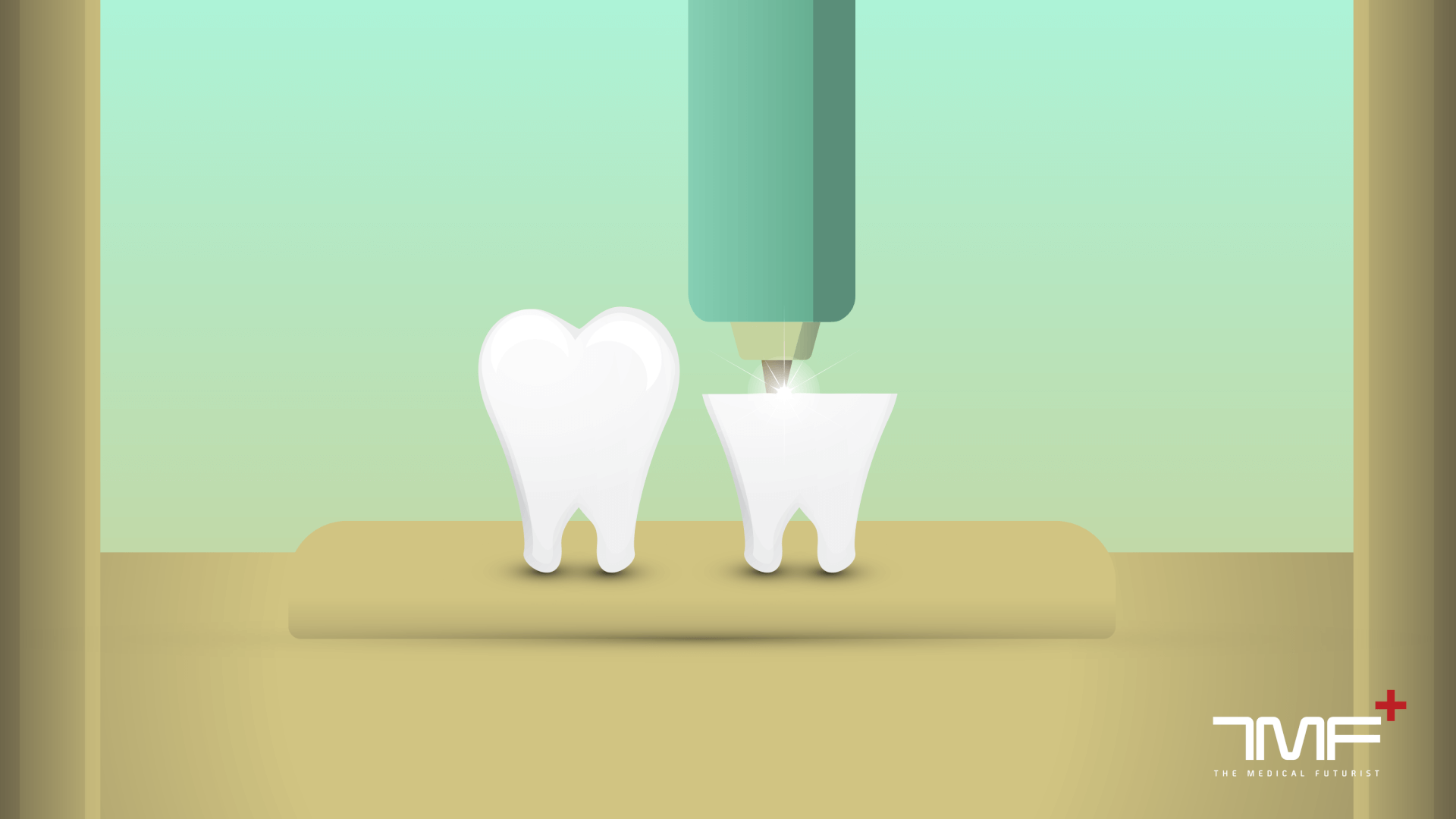
With CAD/CAM technology, the tooth is drilled to prepare it for the crown and a picture is taken with a computer. This image is then relayed to a machine that manufactures the crown right in the office. With a 3D printer doing the hard work, dental labs eliminate the bottleneck of manual modelling and let the business grow. Stratasys, Envisiontech or FormLabs offer such high-tech solutions for dental labs.
3D printers are also able to produce orthodontic models, surgical guides, aligners, retainers and more dental equipment faster and more precisely; tasks that would take longer with traditional methods. This helps in improving workflows, reducing error and the amount of labour needed, which ultimately endows the technology with time and cost-efficiency.
7. Intra-oral camera
One of the greatest inconveniences while being seated in the dentists’ chair is that sometimes, no matter how wide you open your mouth, the dentist still cannot see what they would like to see, even by using the trusty dental mirror. Such situations are not only uncomfortable for both the patient and the doctor, but also painful. However, the advent of intra-oral cameras can remedy this exact problem.
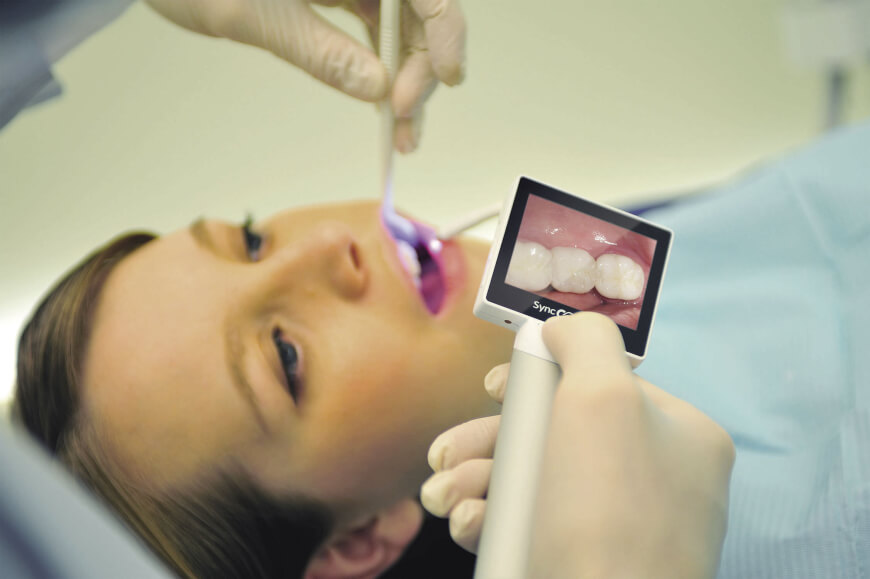
MouthWatch, Dürrdental and Carestream Dental are some of the many companies to have launched intra-oral cameras on the market. The latter promises revolutionary cameras, which are real “patient conversation starters.” The cameras’ unique liquid lens technology works like the human eye to ensure effortless image capture to deliver clear, detailed images patients can really understand.
8. Regenerative dentistry
We’ve come to expect to have our teeth fall off with age or with damage and have them replaced by prostheses. However, the field of regenerative dentistry challenges this preconceived idea with developments that can lead to self-healing teeth and biological therapy for damaged teeth.
Previously, researchers from the University of Nottingham and Harvard University developed dental fillings that allow teeth to heal themselves. These fillings stimulate stem cells to promote the growth of dentin, or the main constituent of our teeth. This effectively enables patients to regrow teeth damaged through dental disease and potentially eliminate the need for root canals!
New discoveries from researchers at Karolinska Institutet in 2020 can accelerate development in the field of regenerative medicine. They were able to map the differentiation pathways of the cells that make up human teeth. They also discovered new cell types and cell layers in teeth that can impact tooth sensitivity.
Isn’t it exciting to think that you might not need to have false teeth to replace your own when you are old, but you might grow new ones? The tooth-fairy will be very excited, for sure!
9. CRISPR
CRISPR is a ground-breaking genome editing method offered by Mother Nature herself, but researchers have discovered its immense potential only recently. As explored in our dedicated articles, it might become the ultimate weapon against cancer or, more controversially, help design babies in the future. And the field of dentistry will also benefit from the technology as well.
So what could CRISPR achieve in dentistry? Well quite a lot, in fact. Chinese researchers are conducting studies with the technology to isolate and switch off oral cancer-associated genes. Other researchers are using CRISPR to alter the functioning of bacteria responsible for plaque formation. Their endeavour could even lead to the reduction or outright prevention of dental caries and periodontal disease. But please don’t give up on brushing your teeth just yet!
The bright future of dental medicine
It is amazing how more and more disruptive innovations will be at our disposal – either for improving oral health as a patient or upgrading our practice as a professional. Our task at The Medical Futurist is to follow the latest innovations and keep pace with the growing possibilities in healthcare.
By medicalfuturist.com





























Leave a Reply